
Amharic Alphabet
The Amharic alphabet, also known as the Fidel (ፊደል), is a writing system used for the Amharic language, which is the official working language of Ethiopia. It is part of the Ge'ez script, an ancient script that originated in the Horn of Africa and is also used for several other Ethiopian and Eritrean languages, such as Tigrinya and Ge'ez (the liturgical language of the Ethiopian Orthodox Church).
The Amharic alphabet is the only actively used native African writing system and the official Ethiopian alphabet. The alphabet consists of 31 consonant letters each of which has seven variations. These variations are created by appending a vowel to each consonant, to make up the syllabary of around 500 Amharic letters.
In addition to the 31 consonants and their variations, the Amharic Fidel has five vowels and its own numeral system. The alphabet includes nine punctuation marks: section mark, colon, word separator, semicolon, question mark, comma, paragraph separator and period.
Key Features of the Amharic Alphabet
-
Type of Script:
The Amharic alphabet is a syllabary, meaning each symbol represents a syllable instead of just a single sound (like the letters in the English alphabet). It’s classified as an abugida, where characters combine consonants and vowels into a single unit.
-
Structure:
The alphabet has 33 base characters. Each character has 7 variations, representing different vowel sounds, creating more than 230 unique characters.
Example characters: ሀ (ha), ለ (le), መ (me), ሰ (se), ገ (ge), ከ (ke).
-
Direction of Writing:
Unlike other Semitic scripts like Arabic or Hebrew, which are written from right to left, Amharic is written left to right.
-
Numerals:
The Amharic writing system includes its own numerical symbols, distinct from Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3).
Historical Background of the Amharic Alphabet
The Amharic alphabet traces its origins to the ancient Ge'ez script, which dates back over 1,700 years. Originally developed for the Ge'ez language, the script later evolved to accommodate Amharic and other Ethiopian languages starting in the 14th century. To learn more about the history, visit the Origin of the Amharic Alphabet page.
Why Is the Amharic Alphabet Important?
The Amharic alphabet is more than just a writing system—it’s a cornerstone of Ethiopian identity and culture. It’s used in:
- Government: Amharic is the working language of Ethiopia's federal government.
- Religion: The script plays a central role in Ethiopian Orthodox Christian texts.
- Education and Media: It is widely used in schools, newspapers, books, and digital platforms.
How Is the Amharic Alphabet Used Today?
Amharic remains the primary language for over 32 million speakers in Ethiopia and the Ethiopian diaspora. With the increasing support of Unicode, the Amharic alphabet is now widely accessible on websites, social media, and mobile devices, making it easier than ever to learn and use.
Learn the Amharic Alphabet
Learn the basics of the Amharic alphabet, including its letters, numbers, and punctuation. These are key to reading and writing in Amharic. In this section, you'll discover the Amharic script, number system, and how punctuation helps with clear communication. Keep reading to explore each of these important elements.
Amharic / Ethiopian Alphabet
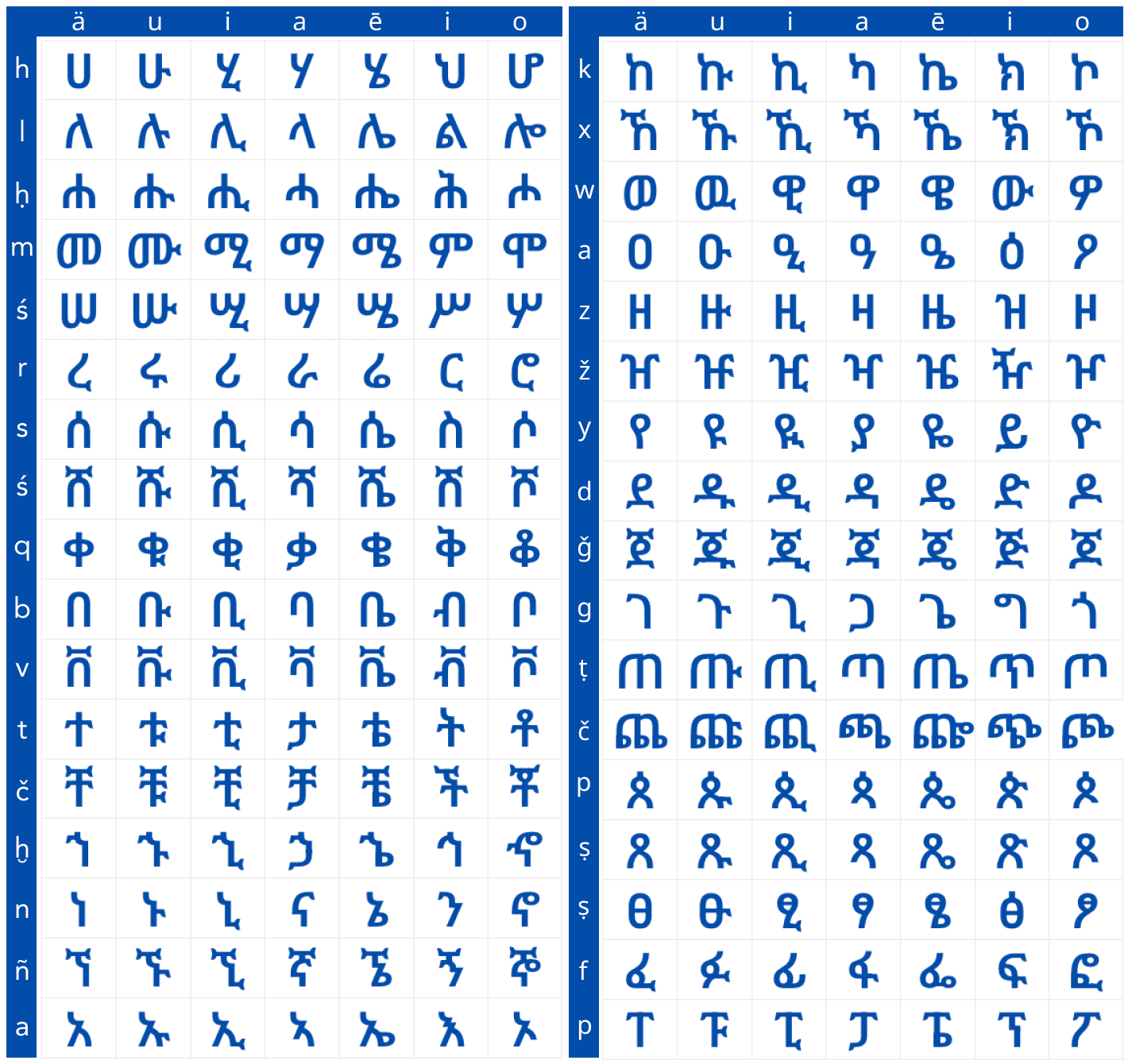
In the Amharic or Ethiopian alphabet, letters are organised in a grid system where consonants appear vertically and their vowel-added variants, horizontally. The grid below shows the Amharic alphabet with english intonation and pronunciations. It offers a simple and quick way of understanding Amharic and getting to comprehend it for the purpose of proper articulation of the language.
Amharic Letters
Amharic Numbers
In addition to consonants and their variants, the alphabet has its own numeral system. All Amharic numbers have two lines on top and bottom which differentiate them from Amharic letters.
Amharic Punctuation
The alphabet also contains unique punctuation marks which are vital in the use of the Amharic language. These include section mark, colon, word separator, semicolon, question mark, comma, paragraph separator and period.
Amharic Orthography
The Amharic alphabet has been transliterated to assign Roman letters to equivalent Amharic letters based on modern Amharic pronunciation. The Transliteration was done in a number of ways within the Latin alphabet such as Encyclopedia Aethiopica’s EAE Transliteration method and the 1967’s UN approved BGN (Board on Geographical Names)/PCGN (Permanent Committee on Geographical Names) transliteration system.
Download Alphabet PDFs
Click the link below to download Alphabet PDF charts to practice on and master the Amharic language in a short time.
